john parker &
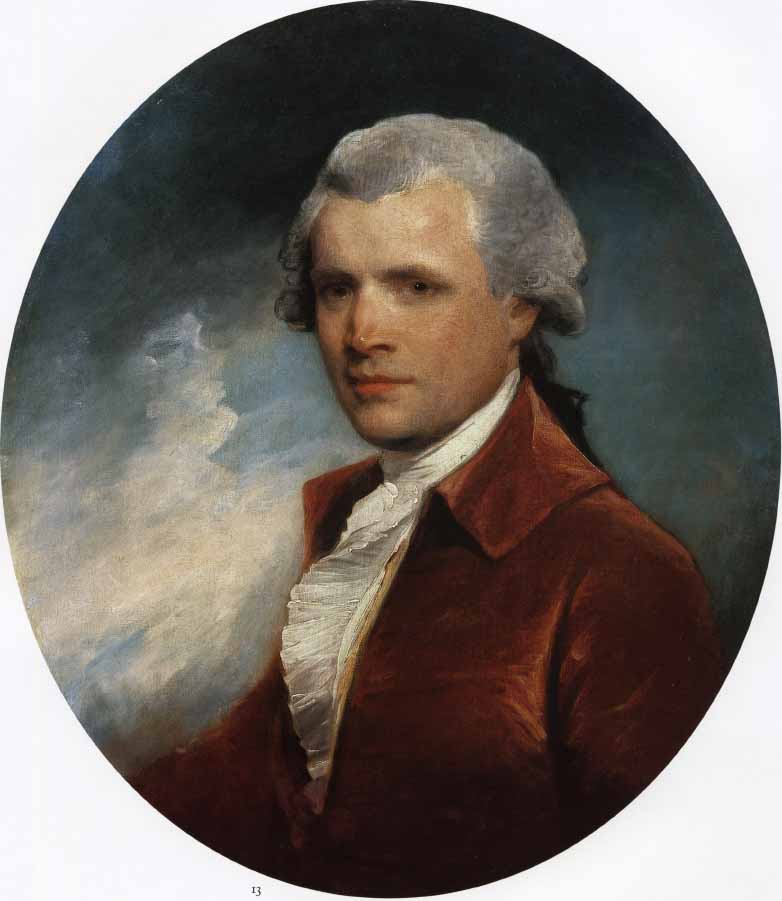


John Singleton Copley was an Anglo-American painter, active in both colonial America and England. He was probably born in Boston, Massachusetts, to Richard and Mary Singleton Copley, both Anglo-Irish. After becoming well-established as a portrait painter of the wealthy in colonial New England, he moved to London in 1774, never returning to America. In London, he met considerable success as a portraitist for the next two decades, and also painted a number of large history paintings, which were innovative in their readiness to depict modern subjects and modern dress. His later years were less successful, and he died heavily in debt.
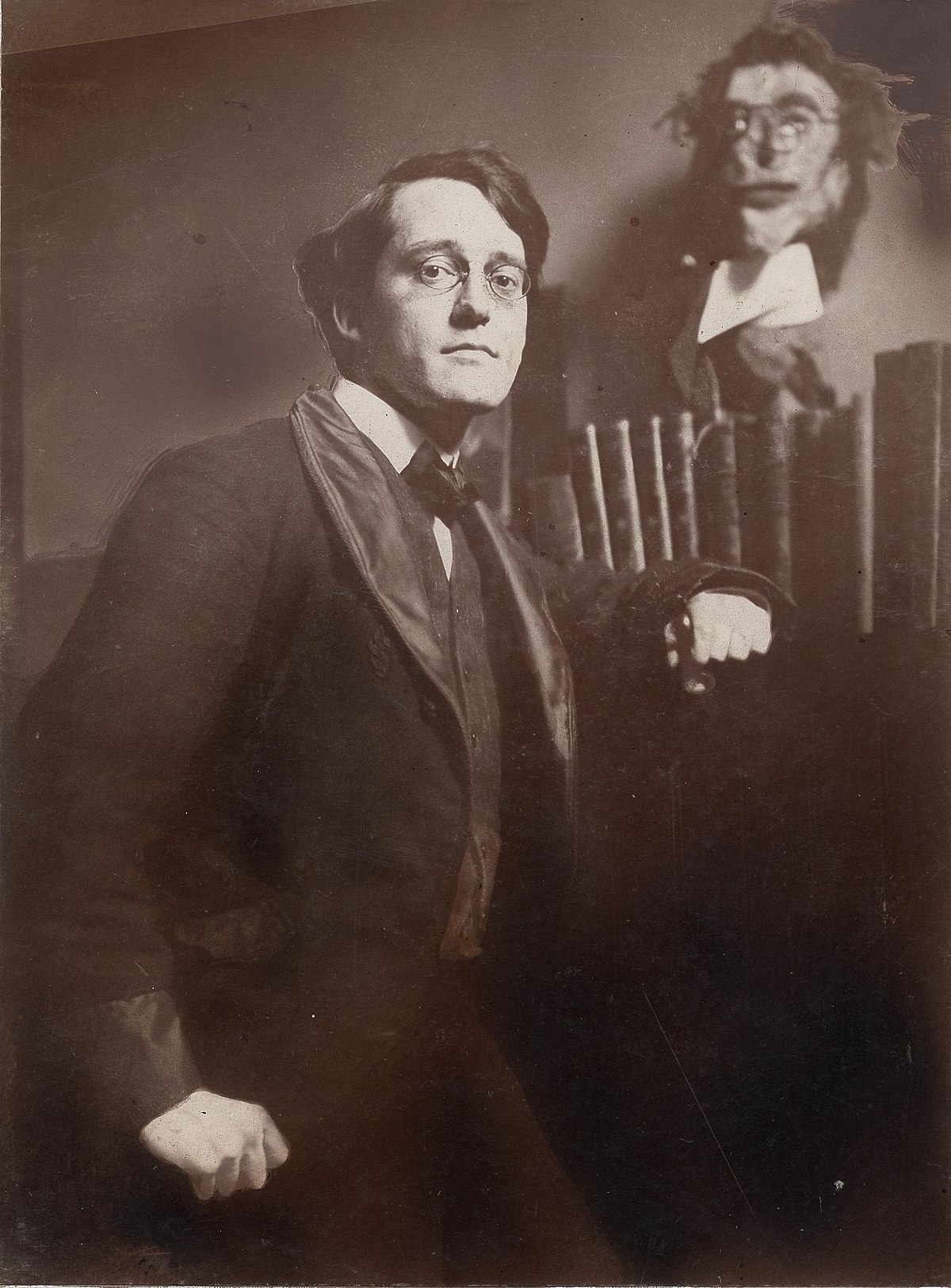


John French Sloan was an American impressionist painter, considered one of the founders of the Ashcan school of American art. He is best known for his urban, everyday genre scenes and his ability to capture the essence of New York City neighborhood life, which he observed from his studio window in Chelsea.
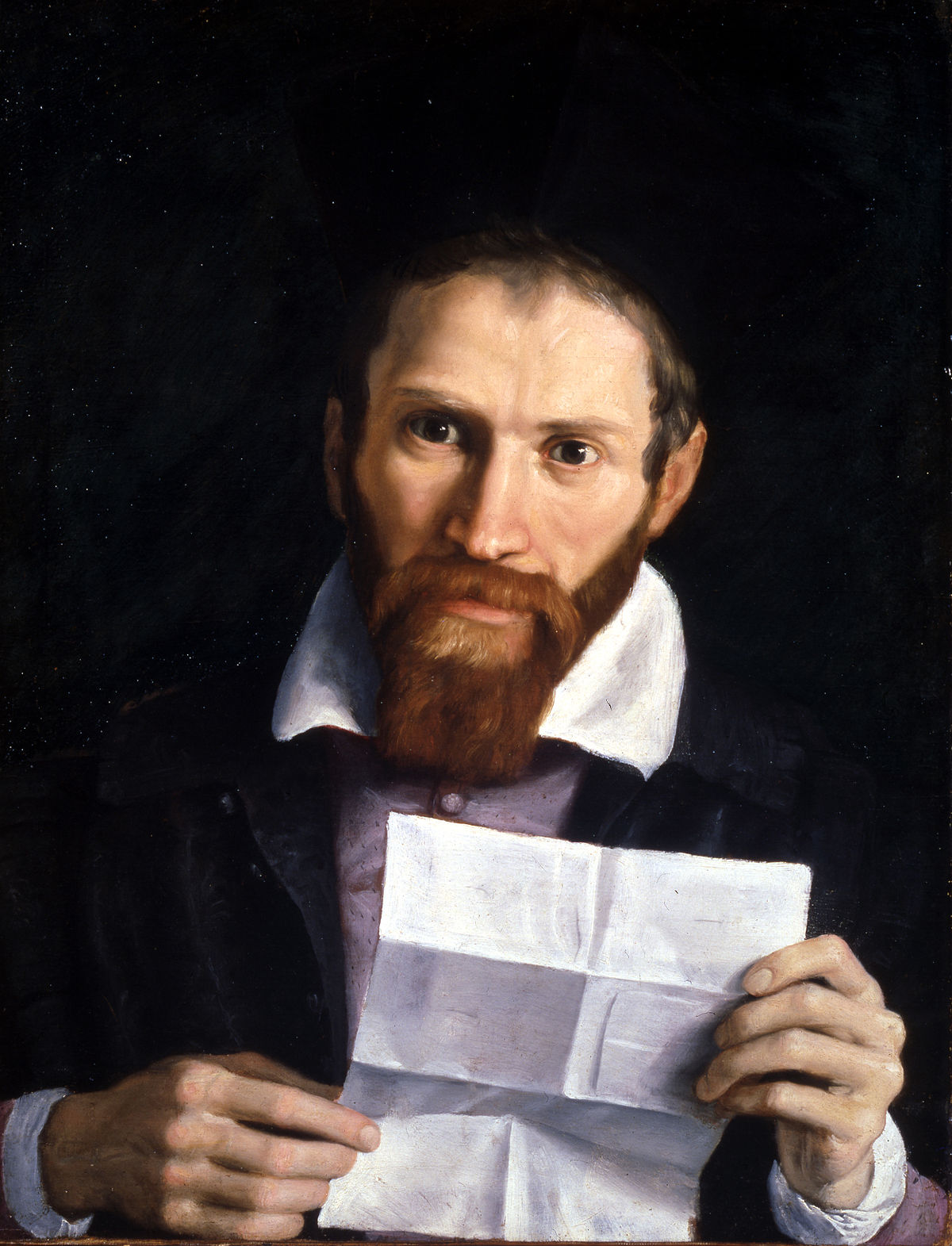


Domenico Zampieri, known as Domenichino, was an Italian Baroque painter who worked in Rome. He was a pupil of the Accademia Carracci in Bologna and was subsequently influenced by the works of Annibale Carracci and Caravaggio.
Domenichino was known for his use of vivid colours, dramatic lighting and his ability to convey emotion in his paintings. He was particularly adept at painting religious subjects and his works often depicted scenes from the life of Christ, the Virgin Mary and saints. He also participated in the fresco decoration of churches and several papal residences, and worked on the decoration of the Palazzo Barberini in Rome.
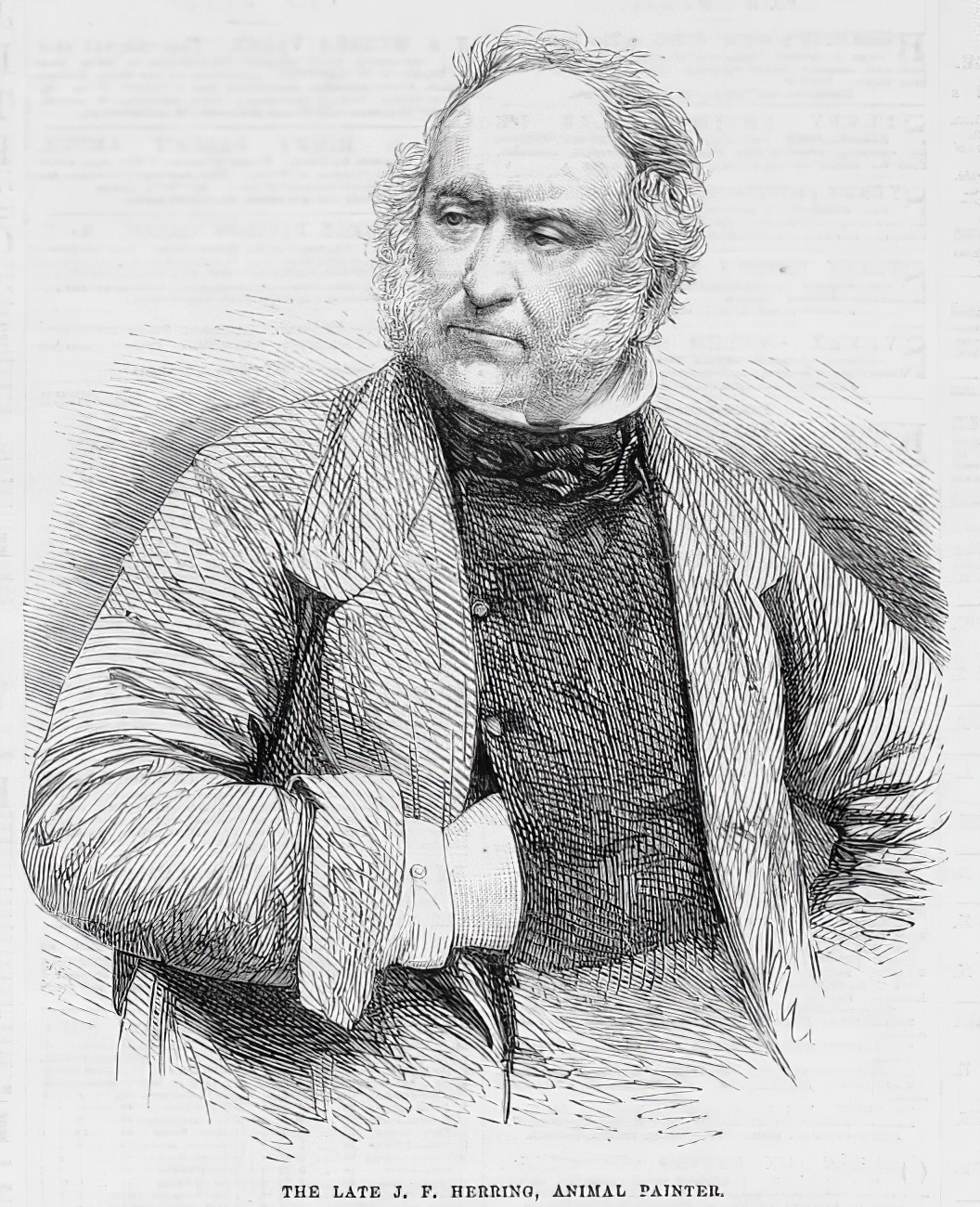


John Frederick Herring the Elder was a British painter of Victorian England.
John had a passion for horses and painting from a young age. In his spare time from his day job as a sign painter and coachman, Herring painted horses for innkeepers and customers. Developing his talent, John specialized in drawing animals and loved to depict sporting events with horses. His impressive and vivid depictions of racehorses, cows and ducks as well as picturesque hunting scenes caught the eye of Queen Victoria. In 1845 Herring was appointed animal painter to Her Royal Highness the Duchess of Kent, followed by a commission from the reigning Queen Victoria, who remained a patron for the rest of his life.
A highly successful and prolific artist, Herring is considered one of the most important animal painters of mid-19th century Europe. He exhibited at the Royal Academy, the British Institution, and the Society of British Artists, where Herring became vice-president in 1842. Three of his sons also became artists.
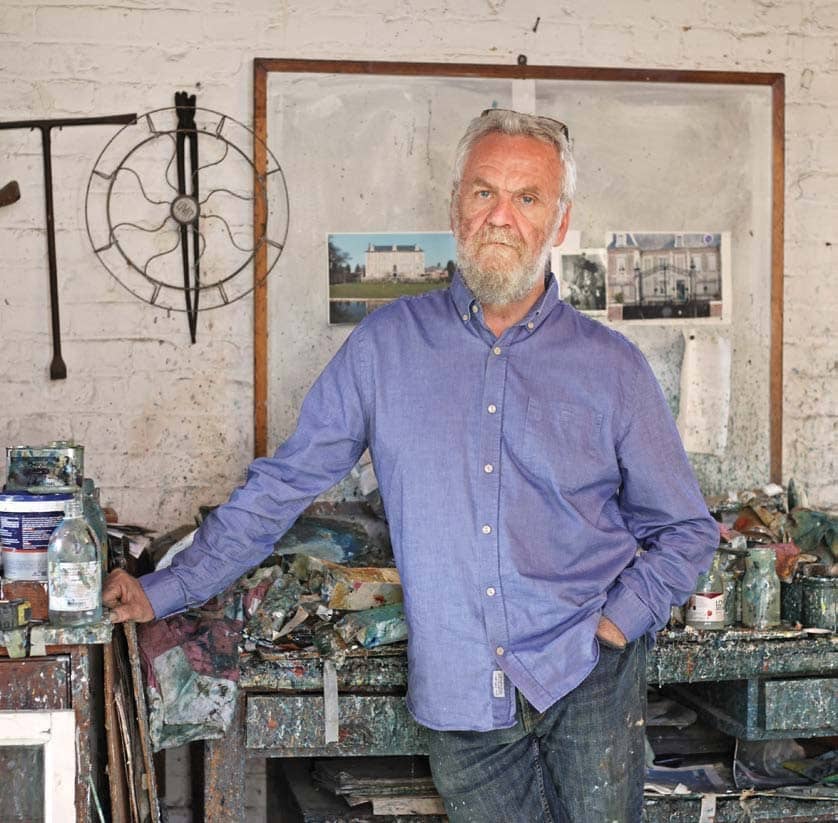
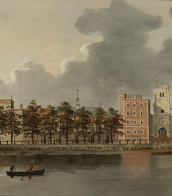

John Monks is an English expressionist painter who lives and works in London and France. Monks is a master of light and shadow. His paintings are often portraits of mysterious abandoned rooms and monumental interiors. Another theme of the artist's work is landscapes.
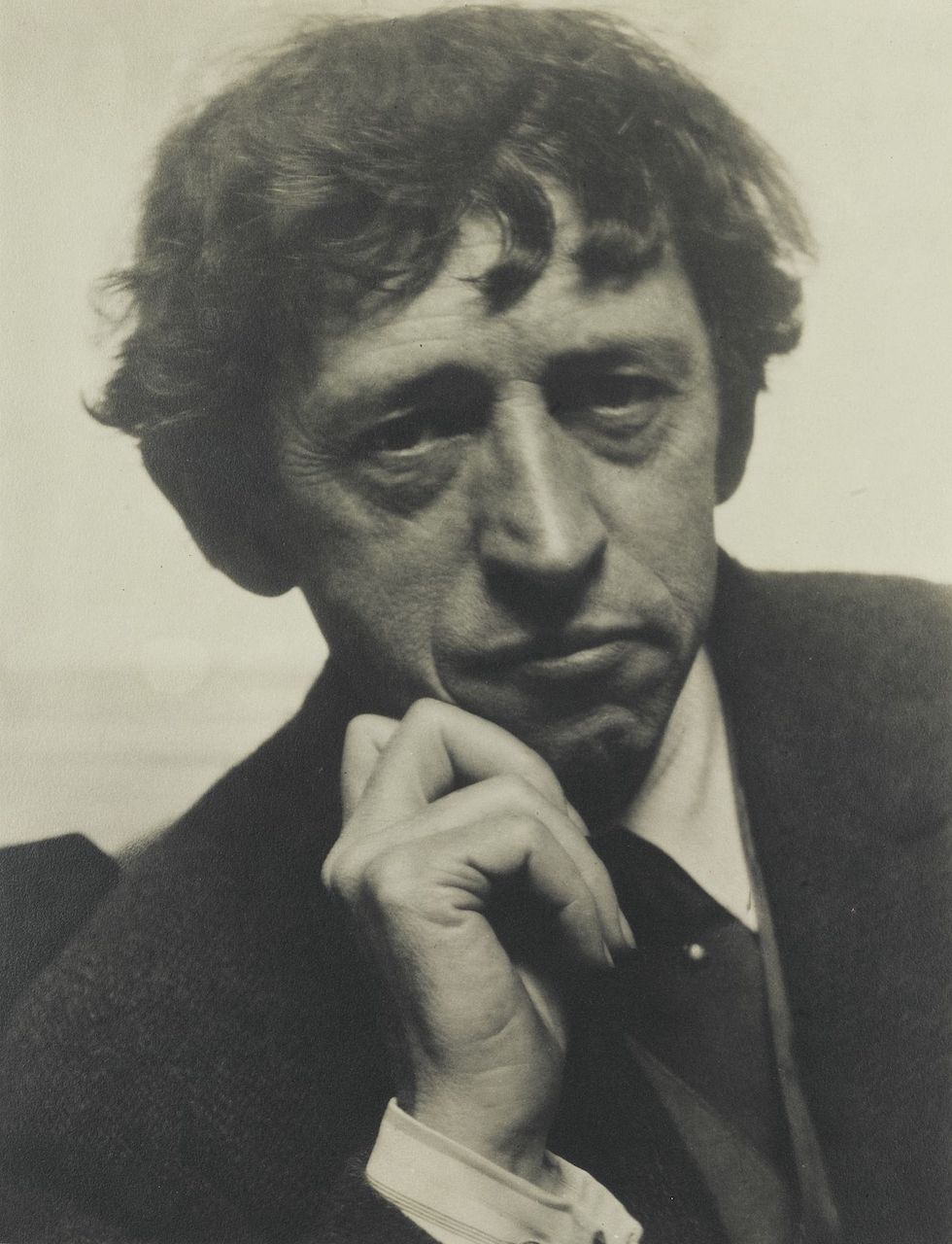


John Marin was an American artist, a prominent member of the first generation of American modernists. He is known for his abstract landscapes and watercolors.
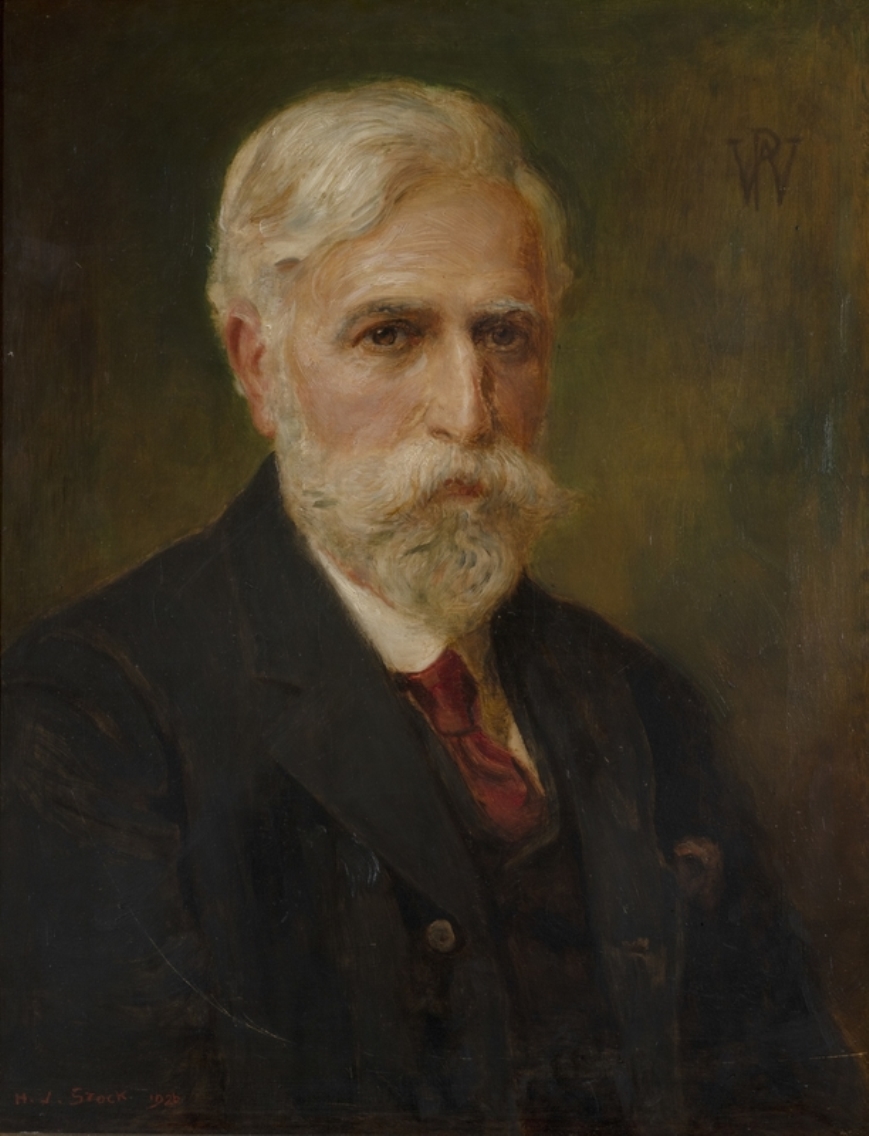


Henry John Stock was a British Pre-Raphaelite painter and representative of the English Romantic tradition.
Henry was nearly blind as a child, but gained his sight when he went to live at Beaulieu in the New Forest. Fully recovered, he attended St. Martin's School of Art and the Royal Academy schools. And apparently the trials of his childhood played a role in the artist's outlook. Stock enjoyed success as a secular portraitist, but his main area of interest has always been fantasy, religious and mythological subjects.
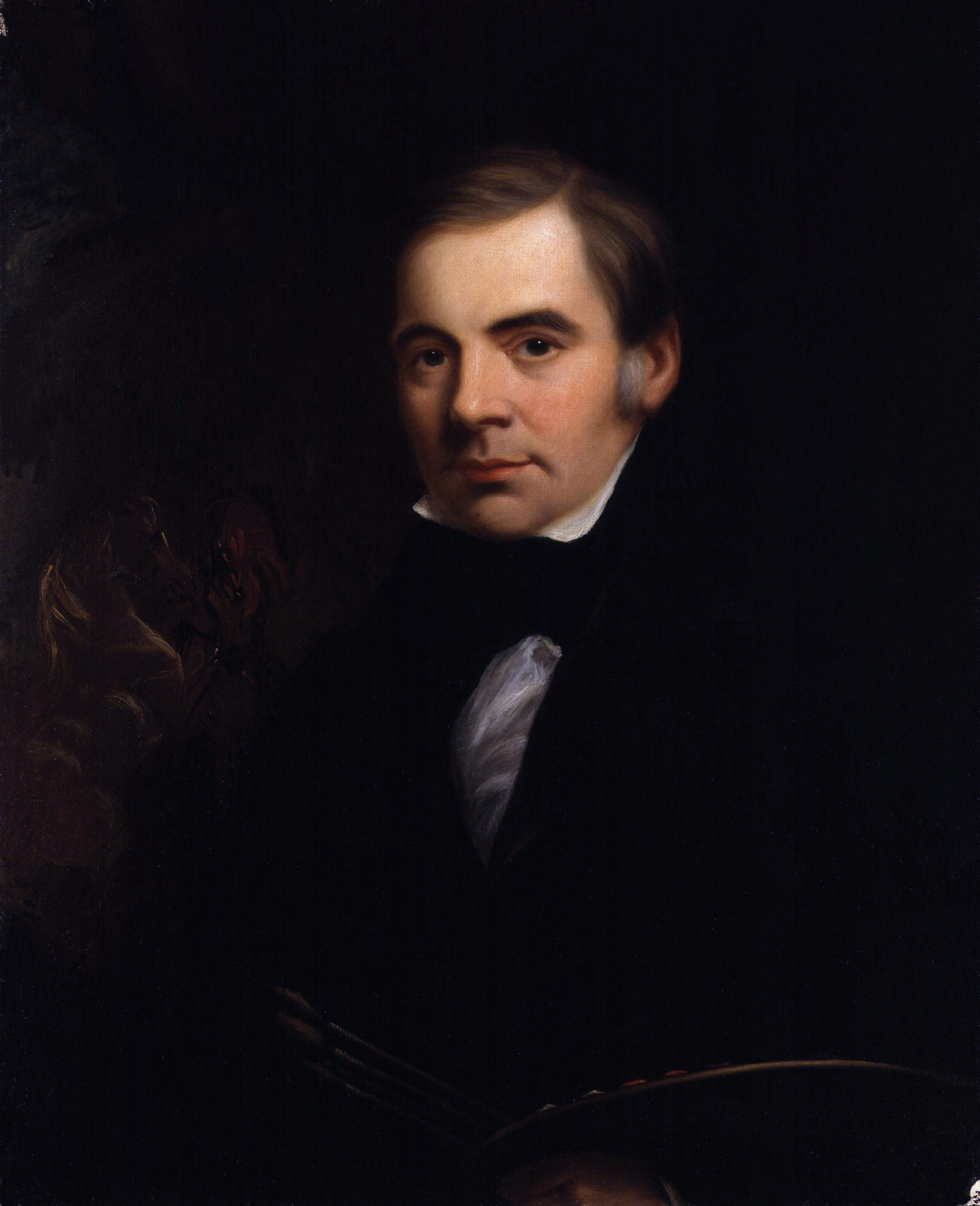


John E. Ferneley was an English artist who specialised in depicting sport horses and hunting scenes. Although his rendition of horses was stylised, he is regarded as one of the great British equine artists, second perhaps only to George Stubbs.
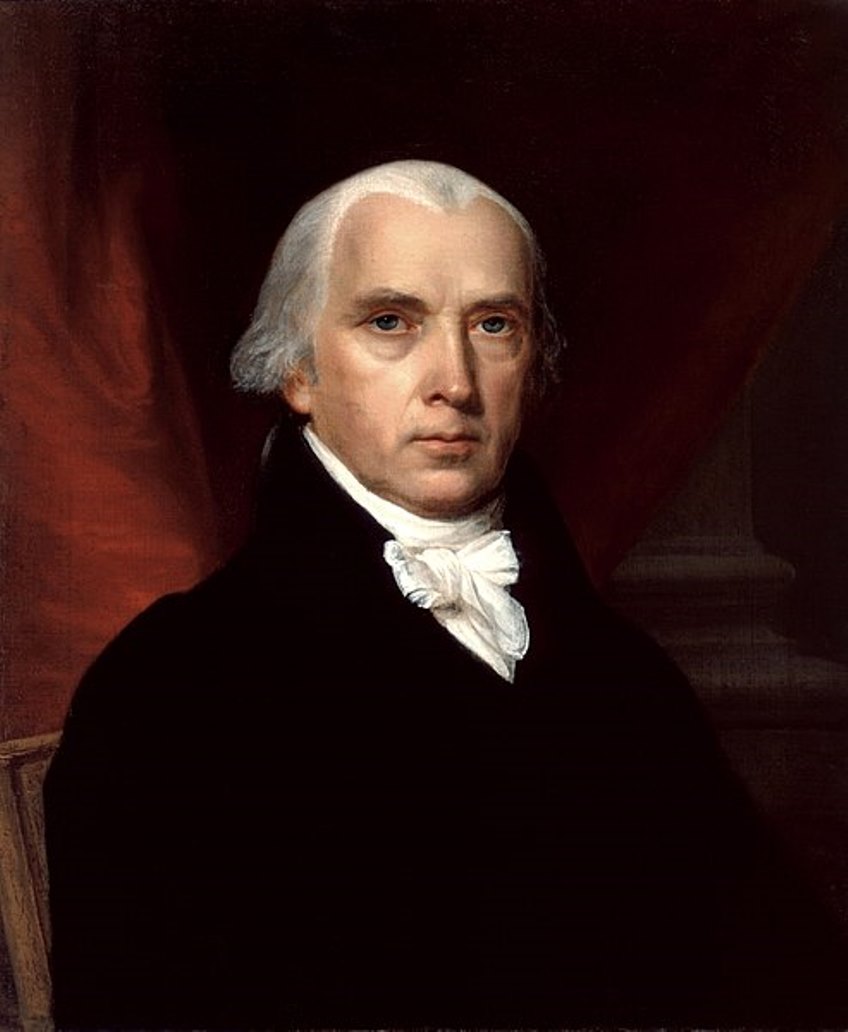


James Madison was an American politician and statesman, the fourth President of the United States (1809-1817).
Madison attended Princeton and studied history, government, and law. He participated in the drafting of the Virginia Constitution in 1776, and in 1780 was chosen to represent Virginia in the Continental Congress (1780-83 and 1786-88). James Madison contributed greatly to the ratification of the Constitution, writing, with Alexander Hamilton and John Jay, The Federalist (1788). He was later called the "father of the Constitution."
In 1792, Madison and Thomas Jefferson (1743-1826) founded the Democratic-Republican Party, which has been called America's first opposition political party. When Jefferson became the third president of the United States, Madison served as his secretary of state. In Congress, he was involved in drafting the Bill of Rights and passing the first revenue legislation. As Secretary of State to President Jefferson (1801-1809), Madison protested to warring France and Great Britain that their seizure of American ships was contrary to international law.
Madison was elected president in 1808, succeeding Jefferson. Continued British interference in shipping, as well as other grievances, led to the War of 1812. During Madison's second term as president, the war was still ongoing, and he and his wife were even forced to flee in the face of advancing British troops who set Washington, D.C. on fire. Despite this, in 1815, the United States declared its victory in the war.
After the end of his second term, Madison remained active in public affairs. He edited his Journal of the Constitutional Convention, was co-chairman of the Virginia Constitutional Convention from 1829-1830, and chancellor of the University of Virginia from 1826-36. He was also Monroe's foreign policy advisor. Although Madison was a slave owner all his life, in the last years of his life he was active in the American Colonization Society, whose mission was to resettle slaves in Africa. James Madison died at the age of 85 in 1836.
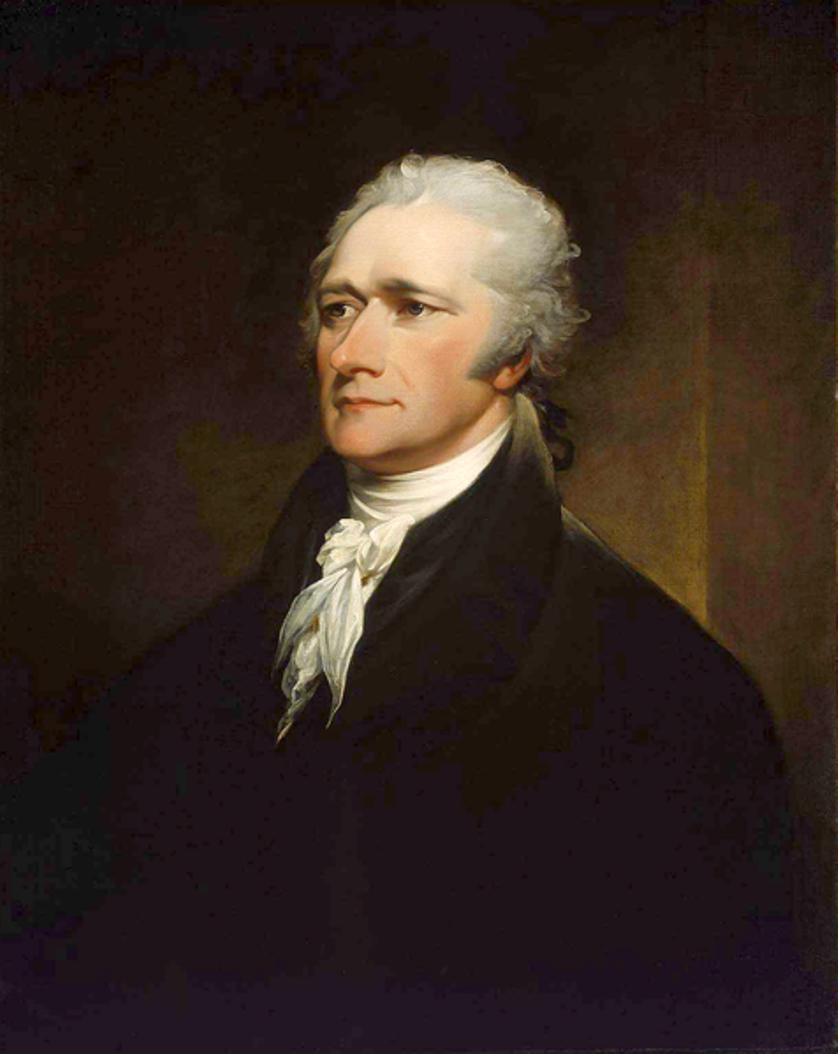

Alexander Hamilton was an American politician and statesman, the founder of the American financial system.
A native of Great Britain, Hamilton arrived in continental America in late 1772 and enrolled at King's College in New York. He became captain of an artillery company in 1776 and fought in the battles of Kips Bay, White Plains, Trenton, and Princeton during the American War of Independence. For four years he served on George Washington's staff as adjutant with the rank of lieutenant colonel. And in 1782, Hamilton was chosen by New York as a delegate to the Confederate Congress.
Alexander Hamilton was also one of New York's delegates to the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia in 1787. He was a passionate advocate of the Constitution and, along with future President James Madison and John Jay, contributed to the famous book The Federalist (1788), writing most of the essays for it. After George Washington was elected the nation's first president in 1789, he appointed Hamilton Secretary of the Treasury. As the first Secretary of the Treasury (1789-1795), Hamilton developed plans to finance the national debt, secure federal credit, encourage the expansion of manufacturing, and organize a federal bank. In 1801, Hamilton founded the New York Evening Post newspaper.
On July 11, 1804, Hamilton was mortally wounded in a duel with his personal and political rival, Vice President Aaron Burr. Today, Alexander Hamilton is revered as one of the founding fathers of the United States, he is known for his role in creating America's financial system, and his portrait is on the ten dollar bill.
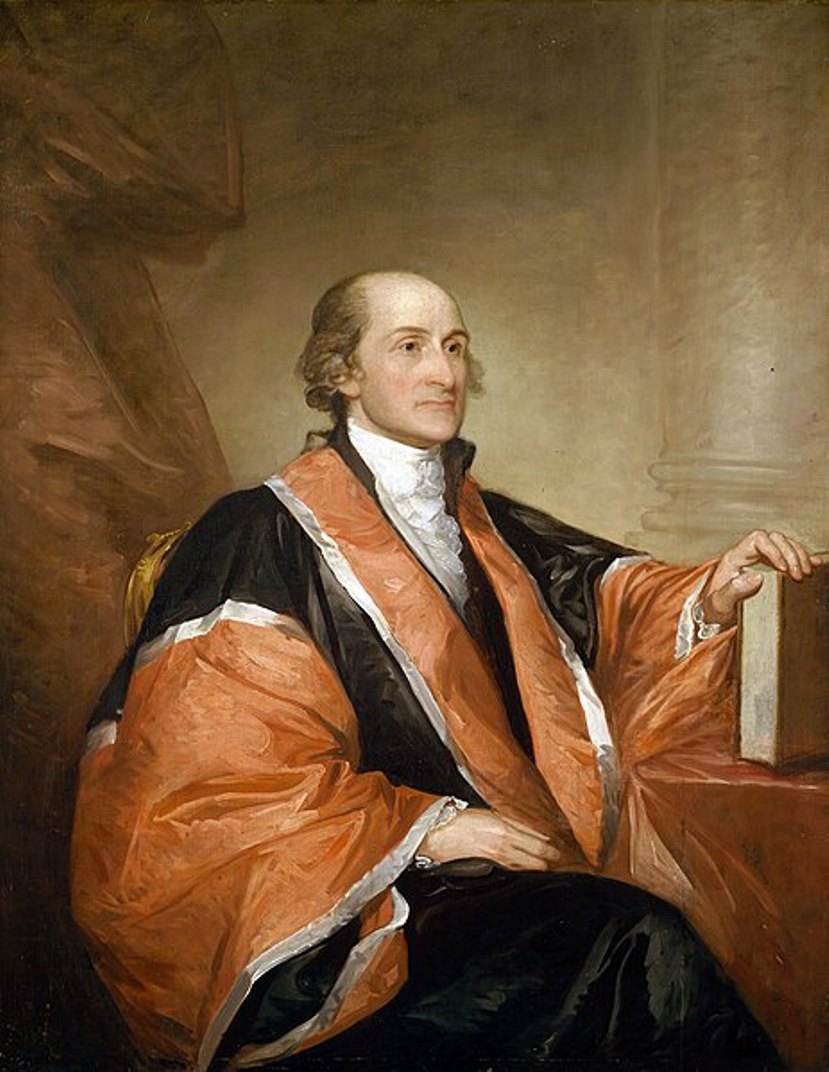

John Jay was an American lawyer and diplomat, statesman, and one of the founding fathers of the United States.
Jay came from French Huguenots, after graduating from King's College (now Columbia University) he entered law school and was admitted to the bar in 1768. After the outbreak of hostilities in the spring of 1775, Jay continued to serve both in New York and in the Continental Congress, which elected him president in late 1778.
In the fall of 1779 he was appointed minister plenipotentiary to Spain, which had recently entered into an alliance with France against England. In May 1782 he traveled to Paris, where a treaty was concluded that formally ended the war with Great Britain in 1783. Before returning to America in July 1784, Jay was appointed secretary of foreign affairs.
In 1788, Jay actively advocated for the ratification of the U.S. Constitution by the state of New York. Together with future President James Madison and economist Alexander Hamilton, he participated in the creation of the famous book The Federalist (1788). Under the new Constitution, President Washington appointed John Jay Chief Justice of the United States in 1789, and in July 1795 he became Governor of New York. After completing his second term as governor in June 1801. Jay retired to his farm in Bedford, New York.

















































![Rare concert handbill for Dizzy Gillespie and ‘His Sextet featuring Charley [sic] Parker’ at Town Hall, New York, Wednesday 16 May 1945](/assets/image/picture_3072052/36fa1/cibsgzqar18fpxqrux3s2u7oixxxbtmom2qqr2v9umvays1xiszpedhzaf25j1692875350jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![Rare concert handbill for Dizzy Gillespie and ‘His Sextet featuring Charley [sic] Parker’ at Town Hall, New York, Wednesday 16 May 1945](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_3072052/36fa1/cibsgzqar18fpxqrux3s2u7oixxxbtmom2qqr2v9umvays1xiszpedhzaf25j1692875350jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)

























